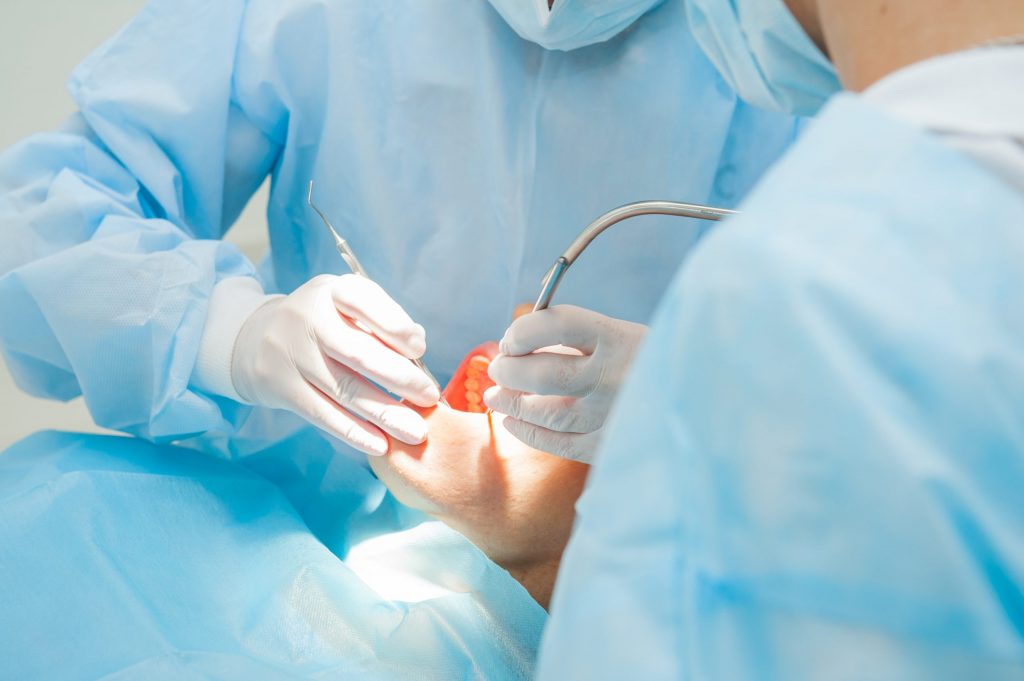
Have you been told you need oral surgery? Or do you wonder if you need it? Whether it’s for cosmetic reasons or a medical need, knowing what to expect can make the experience much less daunting. It’s important to educate yourself so that you can make an informed decision about your next steps.
Answers to Your Top 10 Oral Surgery Questions
From “What is oral surgery?” to “Where to find Philadelphia oral surgeons?” get answers to your most frequently asked oral surgery questions.
 1. What Is Oral Surgery?
1. What Is Oral Surgery?
Oral surgery (also known as maxillofacial surgery) is a type of medical or dental procedure used to treat various problems or abnormalities relating to the mouth, teeth, and jaw. This includes anything from the removal of wisdom teeth to treating facial fractures and malformations of the jaw and mouth. It often requires specialized training outside of general dentistry or medicine.
2. Who Performs Oral Surgery?
Oral surgery is performed by oral and maxillofacial surgeons. These advanced dental specialists have an additional four to eight years of education to focus on the diagnosis and surgical treatment of diseases, injuries, and defects involving both the functional and esthetic aspects of the hard and soft tissues of the oral-maxillofacial region. As such, it requires an in-depth understanding of both dental and medical sciences as well as a broad range of surgical skills. They hold dental and medical degrees.
3. Why Is Oral Surgery Needed?
Oral surgery can be performed for a number of reasons, from treating dental issues caused by trauma or disease to repairing the damage inflicted by oral cancer. It may also be used to improve the cosmetic appearance of the mouth, jaw, and teeth. In addition, it can help prevent further problems down the road by addressing misaligned teeth or improper occlusion (the way teeth come together).
4. What Are the Different Types of Oral Surgery?
 Oral surgery can involve a wide range of treatments and procedures, including:
Oral surgery can involve a wide range of treatments and procedures, including:
- Extractions (removal of teeth or other tissue).
- Restorations (repairing damage to existing teeth).
- Implants (replacing missing teeth).
- Bone grafting (adding new bone material to support dental implants).
- Orthognathic surgery (such as corrective jaw surgery for jaw misalignment and treatment for facial deformities).
- This includes treatment for Temporomandibular Joint disorder (TMJ), cleft palate and cleft lip, and facial trauma surgery.
- Oral pathology services (diagnosing and treating diseases of the mouth).
If you’re curious about what is the most common type of oral surgery, the answer is tooth extraction. Tooth extractions are usually performed when a tooth is beyond repair due to decay or trauma. It can also be used to remove wisdom teeth, which often become impacted and cause severe pain. Other common types of oral surgery include bone grafts, implants, orthognathic surgery, and oral pathology services.
5. What Symptoms Could I Have?
 If you are experiencing any type of pain, discomfort, or swelling around your mouth or jaw area that is not resolving on its own, it could be a sign that you need to see an oral surgeon. Common symptoms that may warrant the need for an oral surgery include:
If you are experiencing any type of pain, discomfort, or swelling around your mouth or jaw area that is not resolving on its own, it could be a sign that you need to see an oral surgeon. Common symptoms that may warrant the need for an oral surgery include:
- Difficulties opening and closing the mouth.
- Pain or tenderness around the jaws, lips, or cheeks.
- Swelling in the face or near the jawline.
- Constant bad breath that is not related to hygiene or diet.
- Difficulty chewing or speaking clearly.
- A lost or damaged tooth.
6. How Long Does It Take?
The amount of time needed for oral surgery depends on the type of procedure being performed. Simple extractions may only take a few minutes, while more complex procedures, such as bone grafts or orthognathic surgery, may require several hours in the operating room. Recovery times vary depending on the type of treatment but can range from a few days to several weeks.
7. Is Oral Surgery Painful?
Many people report minimal pain or discomfort during and after their oral surgery procedure, while others may experience more discomfort. Generally speaking, most oral surgeries are performed with local anesthesia, so patients should not feel any pain during the procedure. Discomfort and swelling after the operation can be managed with pain medications or cold compresses.
8. Are You Put to Sleep for Oral Surgery?
While local anesthesia is used for most oral surgeries, some more complicated procedures (such as impacted wisdom tooth extraction, dental implant surgery, or facial or jaw reconstruction) require the use of general anesthesia.
9. Does Medicaid Cover Oral Surgery?
Medicaid coverage for oral surgery depends on various factors. Eligible individuals may receive coverage for necessary dental care and/or oral surgery, but certain services like cosmetic procedures may not be included. It is important to note that Medicaid rules and coverage guidelines differ by state, so it is wise to contact your local Medicaid office for information on coverage in your area.
10. Where Can I Find Philadelphia Oral Surgeons and Low-cost Oral Surgery?
You can find oral surgery services at Penn Dental Medicine at PHMC on Cedar (PDM at PHMC on Cedar) in Philadelphia, where we specialize in extractions and oral pathology services. Our team of experienced dental professionals is passionate about providing you with affordable options for quality care. We understand how important it is to have access to low-cost oral surgery and are committed to providing you with excellent care that’s within your budget.
Your care is provided by predoctoral students and dental residents from The University of Pennsylvania School of Dental Medicine under the supervision of licensed, experienced faculty dentists to ensure the highest-quality care.
Contact us today or call us at 855-887-9229 for more information on our oral surgery offerings or to schedule an appointment with one of our knowledgeable team members.