Information Library
Start Reading

When pregnant women wonder “what to expect when they’re expecting,” they may not expect their gums to bleed. And amid all the changes a woman’s body experiences during pregnancy, bleeding gums may seem a minor issue.
Bleeding gums during pregnancy, however, are a symptom of the earliest stage of periodontal disease (gum disease). If left untreated, this condition poses potential risks to both the expectant mother and her unborn child.
Keep reading for an overview of the relationship between periodontal disease and pregnancy.
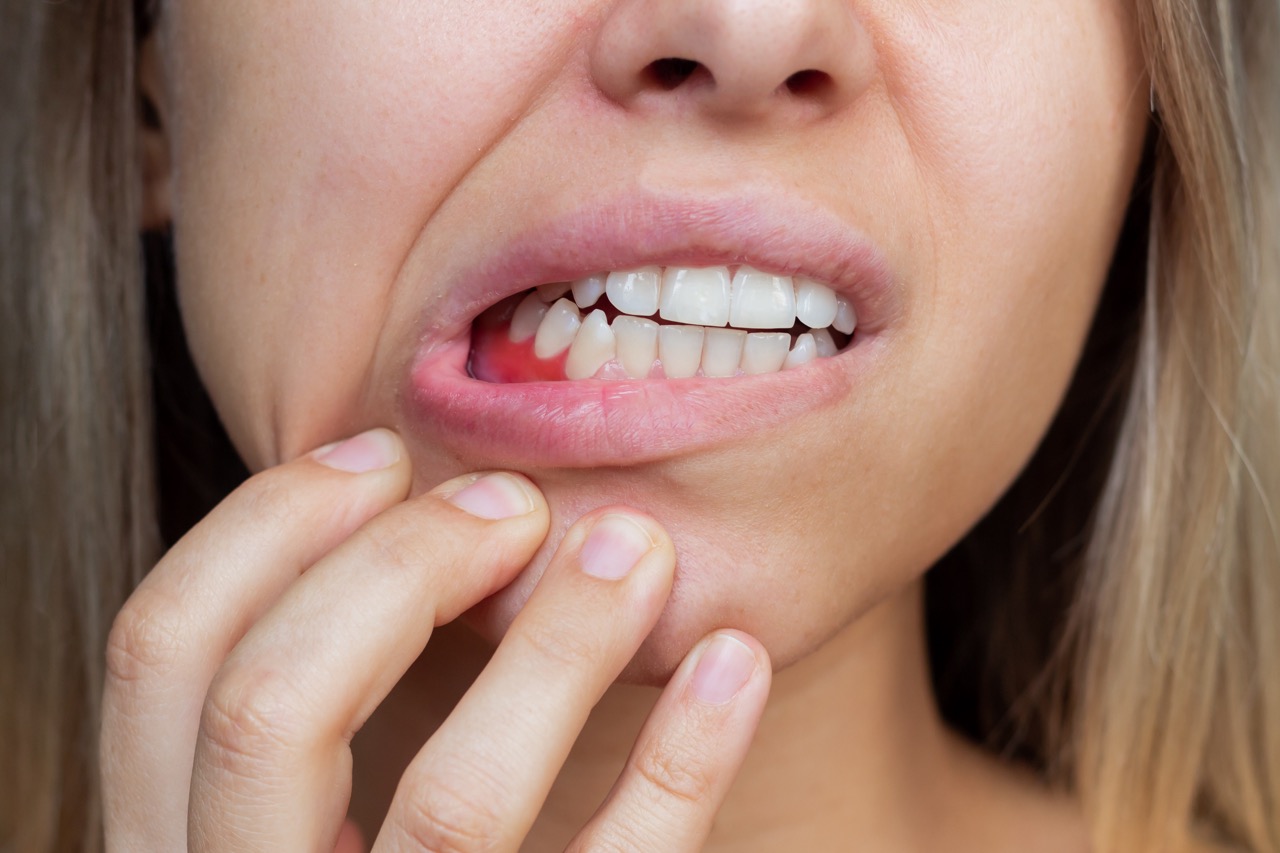

Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease, characterized by tender, swollen, and bleeding gums.
Pregnancy gingivitis is common. Somewhere between 60% and 75% of pregnant women experience it. Pregnancy gingivitis typically begins around the second or third month of pregnancy. It can continue throughout the gestational period.
Why are bleeding gums and pregnancy closely associated?
Hormonal changes in pregnancy—especially increased progesterone levels—can cause gums to become more sensitive and vulnerable to plaque buildup and inflammation. This inflammation, in turn, leads to bleeding while brushing or flossing.
The rise in hormone levels also changes how the body responds to harmful bacteria in the mouth. Normally, the immune system fights off such bacteria to keep the gums healthy. But pregnancy weakens a woman’s immune response, leaving her more vulnerable to bacterial infections like gum disease.
Additionally, hormonal fluctuations can increase women’s risk of pregnancy tumors (pyogenic granulomas). These noncancerous growths typically appear during the second trimester. They are characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. While these tumors aren’t harmful, a dentist should evaluate and treat them to prevent any discomfort or complications.
Another contributing factor to bleeding gums in pregnancy is increased blood volume. The body makes more blood to support both the mother and the developing fetus. The tiny blood vessels in the gums can become more sensitive and prone to bleeding, and the gums can appear swollen.
Poor oral hygiene can exacerbate pregnancy gingivitis, as plaque buildup can further irritate the gums. Many pregnant women, particularly those experiencing morning sickness, find it challenging to keep a consistent dental hygiene routine.
Moreover, certain habits or conditions can make bleeding gums during pregnancy worse. For example, teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism) can put added pressure on the gums and lead to bleeding.
Smoking and consuming tobacco products can also compromise oral health and contribute to gum bleeding. They also pose serious health risks to both mother and unborn child.
Untreated gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of periodontal disease called periodontitis, resulting in tooth loss and other serious oral health complications.
Periodontitis during pregnancy can negatively impact the overall health of both the mother and the developing baby. Research suggests periodontitis in pregnancy is linked to various adverse pregnancy outcomes, including premature birth, low birth weight, and preeclampsia.
How can pregnant women manage bleeding gums during pregnancy?
Brush at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Flossing daily is equally important, as it helps remove plaque and food particles from areas a toothbrush can’t reach. Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can also reduce inflammation and prevent bacterial growth.
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and calcium can promote dental health. Avoiding sugary foods and acidic foods and beverages can help prevent tooth decay and minimize gum irritation. Staying hydrated is essential, too, as it helps maintain saliva flow—a natural defense against oral bacteria.
Expecting mothers should continue to schedule routine checkups with their dentists. Healthy teeth and gums contribute to overall well-being. Dental professionals can assess and treat any existing issues, provide advice on proper oral hygiene practices, and offer recommendations for dental products safe to use during pregnancy.
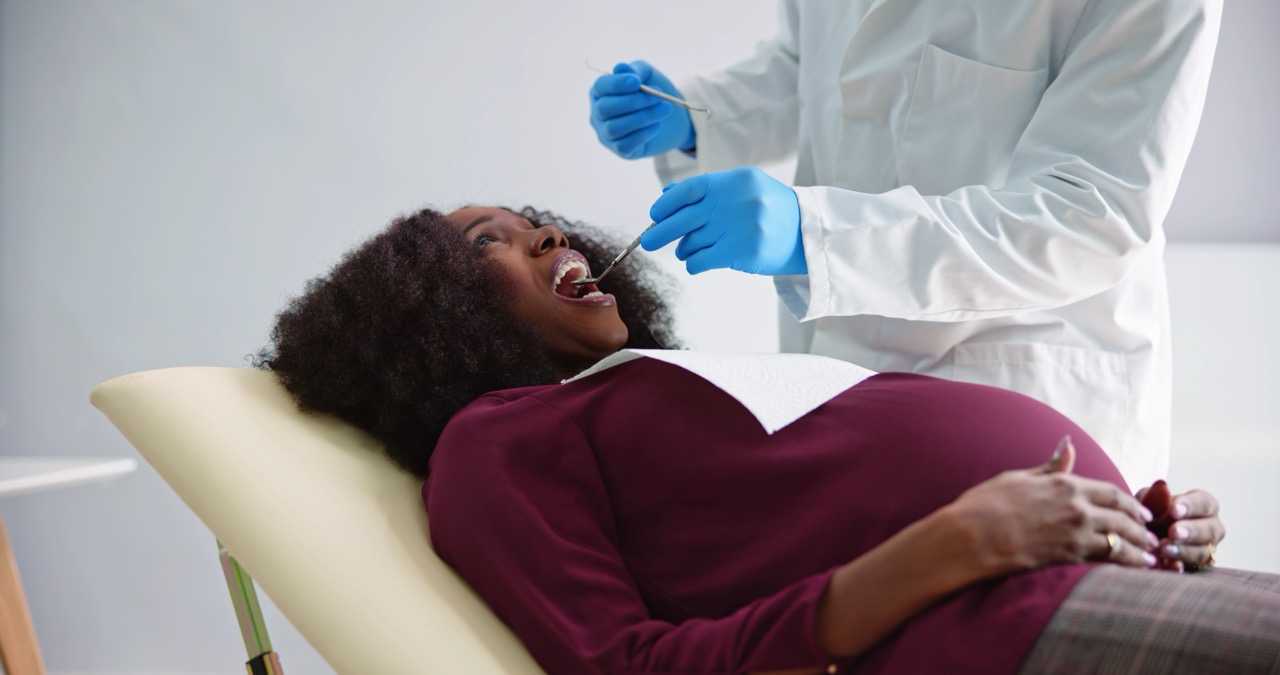
While bleeding gums in pregnancy can be unsettling, the condition is relatively common and, when addressed quickly, highly treatable.
At Penn Dental Medicine (PDM), our skilled dental experts can help you manage periodontal disease during pregnancy. We can help you understand what’s causing your bleeding gums and provide you with the quality, compassionate dental treatments and other care you need to keep your gums healthy.
Your healthy mouth is a vital component of your healthy pregnancy. Trust PDM to help you take the best care of yourself and your baby.
Make your appointment with us online today or call us at 215-898-8965.