Salivary gland disorders are conditions that affect the normal function of the salivary glands, which are responsible for producing saliva in our mouths. These disorders can range from infections and inflammation to tumors and blockages within the glands. While some salivary gland disorders may cause mild symptoms, others can be more severe and require medical intervention. If you suspect you have salivary gland disease, it’s important to speak to your Penn Dental Medicine dentist to determine the best course of action for your situation.
Understanding Salivary Gland Disorders and Treatments
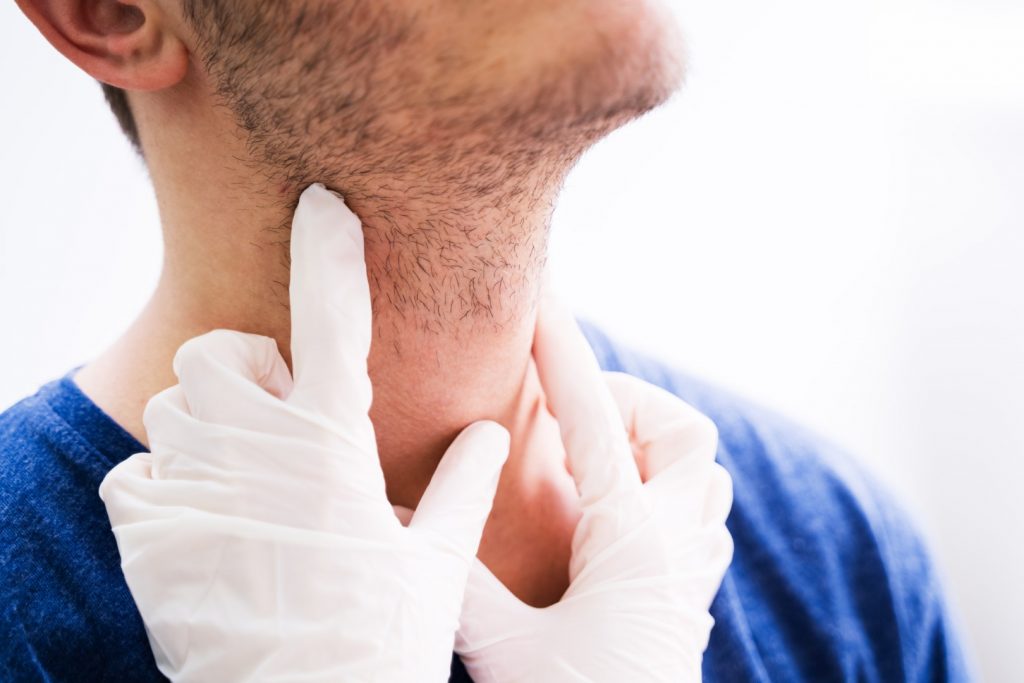 There are three major pairs of salivary glands located in the mouth and throat:
There are three major pairs of salivary glands located in the mouth and throat:
- The parotid glands are situated in front of and just below each ear.
- The submandibular glands are located beneath the lower jaw.
- The sublingual glands are positioned under the tongue.
These glands work together to produce saliva, which helps with chewing, swallowing, and maintaining oral health. In general, most salivary gland disorders happen when the salivary ducts are blocked, which prevents saliva from flowing properly.
What Are the Symptoms of Salivary Gland Disorders?
When the flow of saliva is prevented, it can cause symptoms such as:
- Dry mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Swelling in the affected area.
- Presence of stones or blockages in the ducts.
- Pain.
Infections may also occur if bacteria grow in stagnant saliva within the blocked glands. Additionally, individuals with salivary gland disorders may be more prone to developing cavities and other oral health issues due to the lack of saliva to help protect the teeth and gums.
What Are the Causes of Salivary Gland Disorders?
Salivary gland disorders can be caused by infections from bacteria or viruses, leading to swelling and pain in the affected gland. Inflammation can also result from autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis or other factors that cause the glands to become inflamed and swollen. And, whether benign or malignant, salivary gland tumors can also cause issues with saliva production and flow.
How is Salivary Gland Disorder Diagnosed?
Diagnosing a salivary gland disorder typically involves a thorough examination by a dentist or healthcare provider. This may include feeling for swelling in the affected glands, checking for blockages or stones in the ducts, and possibly ordering imaging tests such as ultrasounds or CT scans to get a better look at the glands. Blood tests may also be conducted to check for signs of infection or inflammation that could be causing the symptoms.
What Are the Most Common Disorders of the Salivary Glands?
 Sialadenitis: This salivary gland infection is usually caused by bacterial infection. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, redness, and fever.
Sialadenitis: This salivary gland infection is usually caused by bacterial infection. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, redness, and fever.
Salivary stones: Also known as sialolithiasis, this condition occurs when small stones form in the ducts of the salivary glands, causing blockages and pain.
Mucoceles: These are cysts that form in the mouth or salivary glands due to blocked saliva flow. They may appear as small, fluid-filled sacs.
Sialadenosis: This is a noninflammatory condition that causes the salivary glands to enlarge without infection or tumor growth. It may be caused by factors such as malnutrition, hormonal imbalances, or certain medications.
Salivary gland tumors: While most salivary gland tumors are benign, some can be cancerous. These tumors may cause symptoms such as swelling, pain, and difficulty swallowing.
What Are Salivary Gland Disorder Treatments?
Treatments depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition.
In cases of infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear up the infection and reduce inflammation. Pain and swelling can be managed with over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications.
For conditions like sialolithiasis, small stones may need to be removed through minimally invasive procedures or surgery such as sial endoscopy or lithotripsy. In more severe cases, the affected gland may need to be surgically removed.
For sialadenosis, addressing the underlying cause, such as improving nutrition or adjusting medications, may help reduce symptoms.
Salivary gland tumors may require a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the type and stage of the tumor.
In some cases, home remedies such as warm compresses, massage, and keeping your mouth moist can help alleviate symptoms and improve saliva flow.
Can Disorders of The Salivary Glands Be Prevented?
 Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly and staying hydrated, can help prevent salivary gland disease, as does avoiding tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption.
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing regularly and staying hydrated, can help prevent salivary gland disease, as does avoiding tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption.
Also, it’s important to seek prompt treatment for any infections or inflammation in the salivary glands to prevent complications. Eating a balanced diet rich in nutrients may help support healthy salivary gland function and reduce the risk of certain conditions like sialadenosis.
Regular dental checkups can also help catch any potential issues with the salivary glands early on. Being aware of any changes in saliva production, swelling, pain, or other symptoms in the mouth or neck area can prompt early detection and treatment of salivary gland disorders.
Treating Salivary Gland Disorders at Penn Dental Medicine
Early detection and treatment are key to preventing long-term complications. If you suspect you may have salivary gland disease, it’s important to see a Penn Dental Medicine oral medicine specialist for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
You can make an appointment by completing this form or calling 215-898-8965. We can help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and provide appropriate care to help you feel better fast.